Comprehensive Financial Planning Outline
Introduction
Financial planning is not just about managing money—it’s about building a future that aligns with your dreams and aspirations. Whether you’re striving for early retirement, securing your family’s financial well-being, or growing your wealth strategically, having a clear roadmap is essential. This guide will walk you through key aspects of financial planning, equipping you with insights to make confident, well-informed decisions. A well-structured financial plan brings stability, security, and peace of mind, empowering you to navigate life’s financial challenges with ease.
1. Executive Summary
- A concise summary of findings, recommendations, and actionable strategies covering cash-flow management, risk/insurance, education, retirement, investment, estate, tax, and special needs planning.
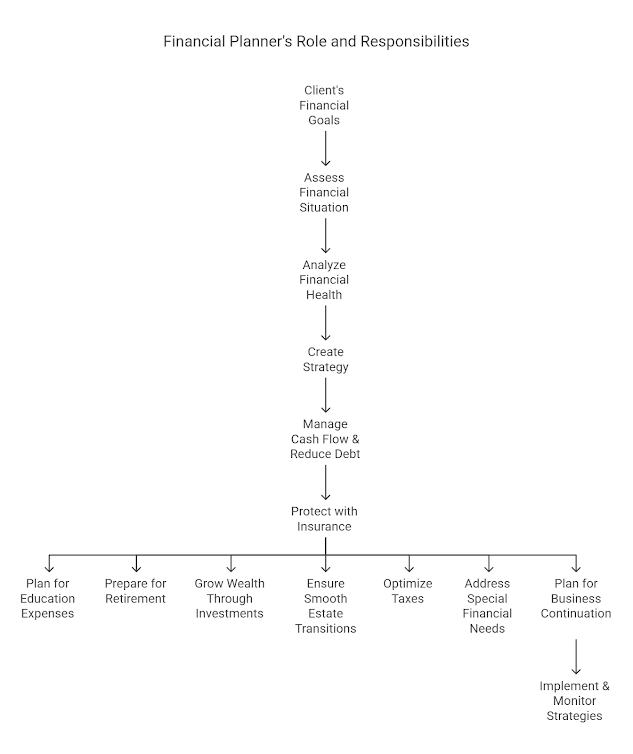
2. Goals and Objectives
- Defining client-specific financial goals and priorities in areas such as cash flow, risk management, education funding, retirement security, investment growth, estate distribution, tax efficiency, and special financial considerations.
3. Personal Data
- Key financial institutions (banks, investment firms, estate agencies, insurance providers, etc.).
- Dependent details (both official and non-official, if applicable).
4. Current Financial Situation
- Analyzing net worth and cash flow efficiency through critical personal finance metrics:
- Liquidity ratio
- Liquid asset to net worth ratio
- Solvency ratio
- Debt-to-asset ratio
- Savings ratio
- Debt servicing ratio
5. Assumptions
- Establishing mutually agreed-upon financial assumptions, including:
- Salary growth projections
- Retirement age expectations
- Dividend yield growth rates
- Inflation rates (official vs. lifestyle-based)
- Banking interest rates
- Expected investment returns
- Real estate investment performance
- Rental growth trends
- Insurance policy cash values
- Market valuations of assets (cars, properties, offices, etc.)
- Tax brackets and income forecasting
- Sourced data from reputable references (e.g., Bank Negara Malaysia, Department of Statistics, EPF/CPF, etc.).
6. Cash-Flow Management
- Implementing strategies based on detailed cash flow analysis:
- Reducing expenses through Pareto analysis and optimization
- Increasing income via diversified revenue streams
- Enhancing asset allocation between liquid and non-liquid assets
- Minimizing liabilities through structured repayment plans
- Measuring progress through personal finance ratios.
- Year-end financial tracking and evaluation.
- Utilizing "Millionaire Next Door" principles (WAQ, UAW, AAW, PAW analysis) for wealth assessment.
7. Risk Management/Insurance Planning
- Identifying and mitigating risks through tailored insurance solutions:
- Life insurance coverage analysis
- Health and hospitalization insurance assessment
- Personal accident protection
- Property and liability insurance strategies (home, vehicle, professional coverage).
- Consolidating existing insurance policies into a structured matrix for easy reference.
8. Education Planning
- Creating an actionable timeline for education funding.
- Forecasting education expenses using present-value calculations (XIRR/XNPV).
9. Retirement Planning
- Structuring a retirement plan using:
- Target replacement ratio and expense methodologies
- Principal liquidation and principal-intact strategies
- Factoring in life expectancy variations.
- Conducting shortfall/excess analysis (NIA vs. required retirement funds).
- Optimizing financial freedom age through Excel Solver modeling.
10. Investment Planning
- Designing an optimized investment portfolio tailored to client-specific goals.
- Allocating assets strategically to balance risk and return.
- Applying Excel Solver for:
- Minimizing portfolio risk for a given ROI target
- Maximizing Sharpe ratio for optimal investment efficiency
11. Estate Planning
- Developing asset distribution strategies through wills, trusts, and power of attorney.
- Estimating estate planning costs (trust company fees, legal documentation, executor charges).
- Ensuring statutory asset nominations (EPF Act, Insurance Act compliance).
12. Tax Planning
- Maximizing tax efficiency through rebates, deductions, and credits.
- Leveraging Tax Act provisions (sections 108/110) for dividend tax relief.
13. Special Needs Planning
- Custom financial planning for individuals with unique needs (e.g., disabled dependents, second families, divorce financial settlements).
14. Business Continuation Planning
- Implementing buy-sell agreements supported by life insurance to ensure seamless business transitions.
15. Recommendations, Implementation & Action Plan
- Establishing a timeline-driven action plan with designated responsible persons (PICs).
- Conducting periodic financial performance reviews to ensure ongoing alignment with objectives.
Conclusion
Your financial journey is a marathon, not a sprint. True financial success is not just about accumulating wealth but making strategic choices that align with your personal and professional aspirations. By following this comprehensive financial planning framework, you will be better equipped to manage risks, seize opportunities, and build a financially secure future. Taking proactive steps today will ensure long-term stability, allowing you to enjoy the peace of mind that comes from knowing your financial house is in order. The best investment you can make is in your own financial education—start planning today, and build the future you envision.
No comments:
Post a Comment